Exact Adaptable Radial Axes (ARA) mappings using the L1 norm
Source:R/ara_exact_l1.R
ara_exact_l1.Rdara_exact_l1() computes exact Adaptable Radial Axes
(ARA) mappings for the L1 norm
Usage
ara_exact_l1(
X,
V,
variable = 1,
solver = "glpkAPI",
use_glpkAPI_simplex = TRUE,
cluster = NULL
)Arguments
- X
Numeric data matrix of dimensions N x n, where N is the number of observations, and n is the number of variables.
- V
Numeric matrix defining the axes or "axis vectors". Its dimensions are n x m, where 1<=m<=3 is the dimension of the visualization space. Each row of
Vdefines an axis vector.- variable
Integer that indicates the variable (in [1,n]) for which the estimates of high-dimensional data will be exact. Default: variable = 1.
- solver
String indicating a package for solving the linear problem(s). It can be "clarabel" (default), "glpkAPI", "Rglpk", or "CVXR".
- use_glpkAPI_simplex
Boolean parameter that indicates whether to use the simplex algorithm (if
TRUE) or an interior point method (ifFALSE), when using the glpkAPI solver. The default isTRUE.- cluster
Optional cluster object related to the parallel package. If supplied, and
n_LP_problemsis N, the method computes the mappings using parallel processing.
Value
A list with the three following entries:
PA numeric N x m matrix containing the mapped points. Each row is the low-dimensional representation of a data observation in X.
statusA vector of length N where the i-th element contains the status of the chosen solver when calculating the mapping of the i-th data observation. The type of the elements depends on the particular chosen solver.
objvalThe numeric objective value associated with the solution to the optimization problem, considering matrix norms.
If the chosen solver fails to map one or more data observations (i.e., fails
to solve the related optimization problems), their rows in P will
contain NA (not available) values. In that case, objval will
also be NA.
Details
ara_exact_l1() computes low-dimensional point representations of
high-dimensional numerical data (X) according to the data
visualization method "Adaptable Radial Axes" (M. Rubio-Sánchez, A. Sanchez,
and D. J. Lehmann (2017), doi: 10.1111/cgf.13196), which
describes a collection of convex norm optimization problems aimed at
minimizing estimates of original values in X through dot products of
the mapped points with the axis vectors (rows of V). This particular
function solves the constrained optimization problem in Eq. (13), for the L1
vector norm. Its equality constraint forces estimates to be exact for one of
the data variables.
References
M. Rubio-Sánchez, A. Sanchez, D. J. Lehmann: Adaptable radial axes plots for improved multivariate data visualization. Computer Graphics Forum 36, 3 (2017), 389–399. doi:10.1111/cgf.13196
Examples
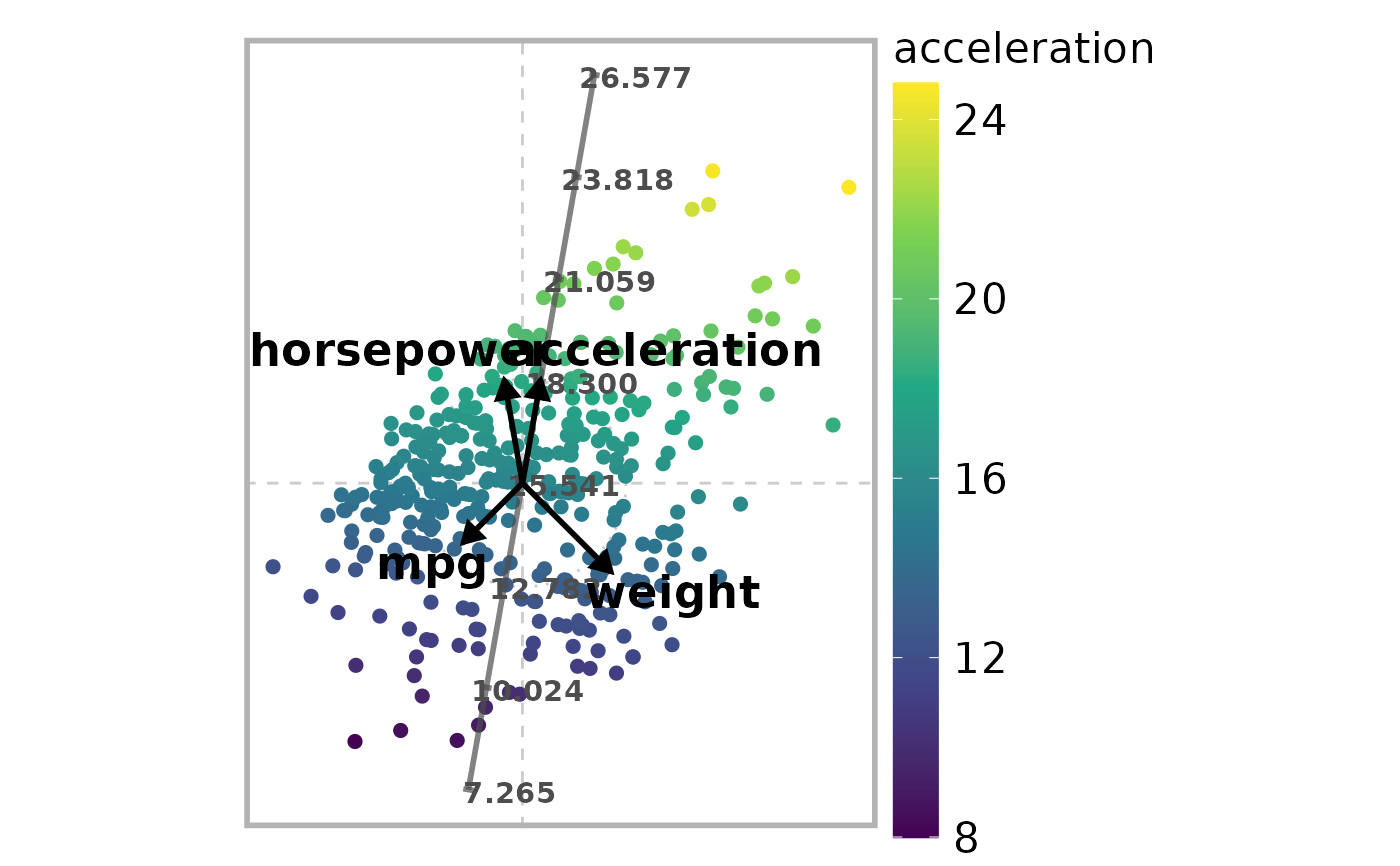
# Define subset of (numerical) variables of the auto_mpg dataset
# 1:"mpg", 4:"horsepower", 5:"weight", 6:"acceleration"
selected_variables <- c(1, 4, 5, 6)
n <- length(selected_variables)
# Retain only selected variables and rename dataset as X
X <- auto_mpg[, selected_variables] # Select a subset of variables
# Remove rows with missing values from X
N <- nrow(X)
rows_to_delete <- NULL
for (i in 1:N) {
if (sum(is.na(X[i, ])) > 0) {
rows_to_delete <- c(rows_to_delete, -i)
}
}
X <- X[rows_to_delete, ]
# Convert X to matrix
X <- apply(as.matrix.noquote(X), 2, as.numeric)
# Standardize data
Z <- scale(X)
# Define axis vectors (2-dimensional in this example)
r <- c(0.8, 1, 1.2, 1)
theta <- c(225, 100, 315, 80) * 2 * pi / 360
V <- pracma::zeros(n, 2)
for (i in 1:n) {
V[i,1] <- r[i] * cos(theta[i])
V[i,2] <- r[i] * sin(theta[i])
}
# Select variable for exact estimates, and use it for coloring the embedded
# points
variable <- sample(1:n, 1)
# Set the number of CPU cores/workers
# NCORES <- parallelly::availableCores(omit = 1)
# NCORES <- max(1,parallel::detectCores() - 1)
NCORES <- 2L
# Create a cluster for parallel processing
cl <- parallel::makeCluster(NCORES)
# Compute the mapping
mapping <- ara_exact_l1(
Z,
V,
variable = variable,
solver = "glpkAPI",
use_glpkAPI_simplex = TRUE,
cluster = cl
)
# Stop cluster
parallel::stopCluster(cl)
# Select variables with labeled axis lines on ARA plot
axis_lines <- variable
# Draw the ARA plot
draw_ara_plot_2d_standardized(
Z,
X,
V,
mapping$P,
axis_lines = axis_lines,
color_variable = variable
)