Draws a 2D Adaptable Radial Axes (ARA) plot for standardized data
Source:R/draw_ara_plot.R
draw_ara_plot_2d_standardized.RdCreates a plot associated with an Adaptable Radial Axes (ARA) mapping
Arguments
- Z
Standardized numeric data matrix of dimensions N x n, where N is the number of observations, and n is the number of variables.
- X
Original numeric data matrix (before standardizing) of dimensions N x n
- V
Numeric matrix of "axis vectors" of dimensions n x 2, where each row of
Vdefines an axis vector.- P
Numeric data matrix of dimensions N x 2 containing the N 2-dimensional representations of the data observations (i.e., the embedded points).
- weights
Numeric array specifying non-negative weights associated with each variable. Can also be a 1D matrix. Default: array of n ones.
- axis_lines
Array of integer variable indices (in [1,n]) indicating which calibrated axis lines are to be displayed. Default: NULL.
- color_variable
Integer (in [1,n]) that indicates the variable used to color the embedded points. Default: NULL.
Details
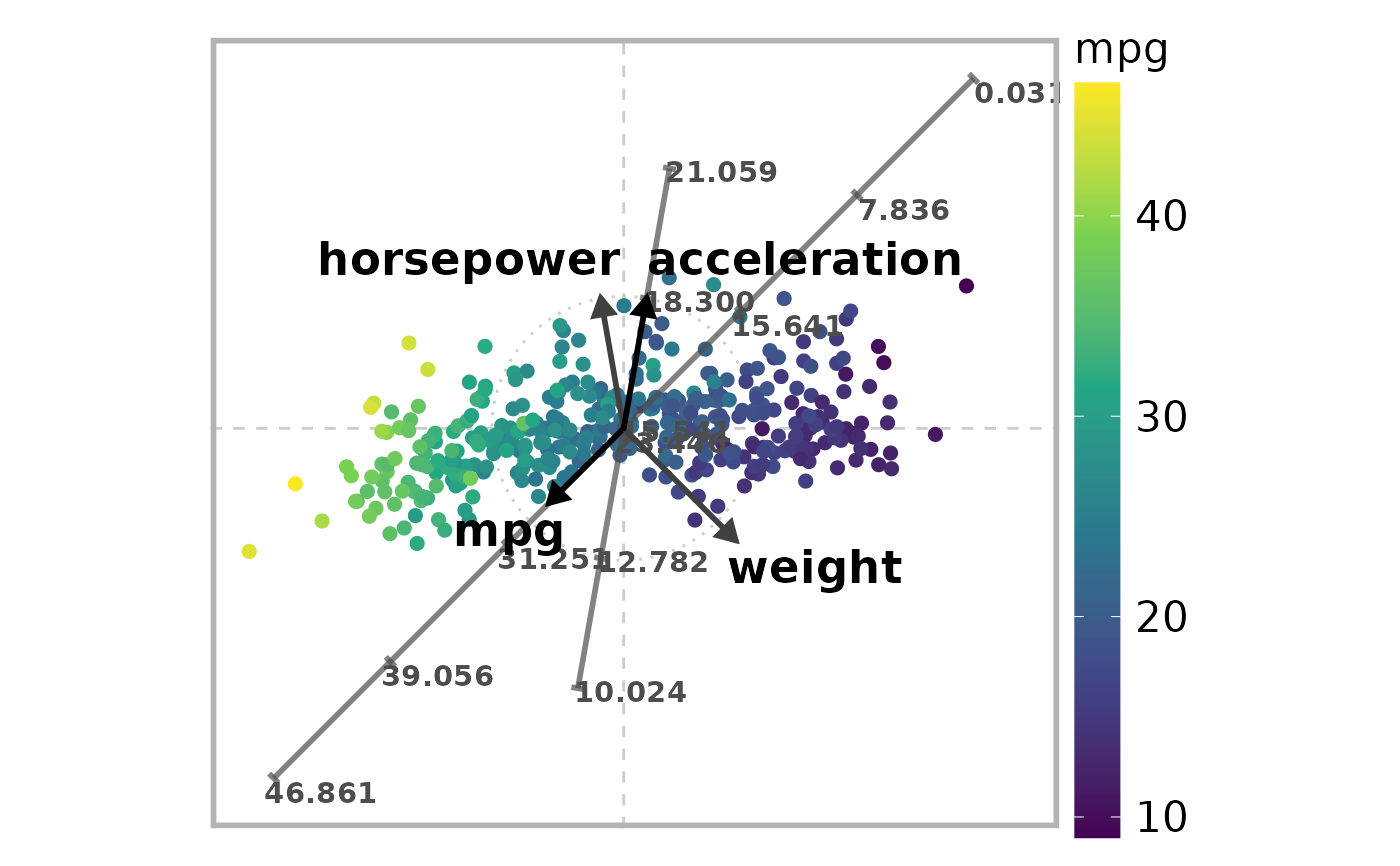
The function draw_ara_plot_2d_standardized() generates a basic
two-dimensional plot related to an "Adaptable Radial Axes" (ARA) mapping
(M. Rubio-Sánchez, A. Sanchez, and D. J. Lehmann (2017), doi:
10.1111/cgf.13196) for high-dimensional numerical data (X) that has
been previously standardized (Z). The plot displays a set of 2D points
(P), each representing an observation from the high-dimensional
dataset. It also includes a collection of axis vectors (V), each
corresponding to a specific data variable. If the ARA mapping incorporates
weights (weights), these axis vectors are colored accordingly to
reflect the weighting. For a user-specified subset of variables
(axis_lines), the function additionally draws axis lines with tick
marks that represent values of the selected variables. Users can estimate the
values of the high-dimensional data by visually projecting the plotted points
orthogonally onto these axes. The plotted points can also be colored
according to the values of the variable color_variable.
References
M. Rubio-Sánchez, A. Sanchez, D. J. Lehmann: Adaptable radial axes plots for improved multivariate data visualization. Computer Graphics Forum 36, 3 (2017), 389–399. doi:10.1111/cgf.13196
Examples
# Define subset of (numerical) variables
# 1:"mpg", 4:"horsepower", 5:"weight", 6:"acceleration"
selected_variables <- c(1, 4, 5, 6)
n <- length(selected_variables)
# Retain only selected variables and rename dataset as X
X <- auto_mpg[, selected_variables] # Select a subset of variables
# Remove rows with missing values from X
N <- nrow(X)
rows_to_delete <- NULL
for (i in 1:N) {
if (sum(is.na(X[i, ])) > 0) {
rows_to_delete <- c(rows_to_delete, -i)
}
}
X <- X[rows_to_delete, ]
# Convert X to matrix
X <- apply(as.matrix.noquote(X), 2, as.numeric)
# Standardize data
Z <- scale(X)
# Define axis vectors (2-dimensional in this example)
r <- c(0.8, 1, 1.2, 1)
theta <- c(225, 100, 315, 80) * 2 * pi / 360
V <- pracma::zeros(n, 2)
for (i in 1:n) {
V[i,1] <- r[i] * cos(theta[i])
V[i,2] <- r[i] * sin(theta[i])
}
# Define weights
weights <- c(1, 0.75, 0.75, 1)
# Compute the mapping
mapping <- ara_unconstrained_l2(Z, V, weights = weights, solver = "formula")
# Select variables with labeled axis lines on ARA plot
axis_lines <- c(1, 4) # 1:"mpg", 4:"acceleration")
# Select variable used for coloring embedded points
color_variable <- 1 # "mpg"
# Draw the ARA plot
draw_ara_plot_2d_standardized(
Z,
X,
V,
mapping$P,
weights = weights,
axis_lines = axis_lines,
color_variable = color_variable
)